-
NewsA Duke Forest tour featured research from the SEEDS Lab.
-
NewsUrban ecologists developed a new approach to understanding biodiversity patterns in cities. The work could inform efforts to improve access to nature’s benefits.
-
NewsModeling experiments show Pacific warm and cold patches persisted even when continents were in different places
-
NewsReforestation in low- and middle-income countries can remove up to 10 times more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere at lower cost than previously estimated, making it a potentially more effective option to fight climate change.
-
NewsExchangeable manganese cuts carbon storage in boreal forests
-
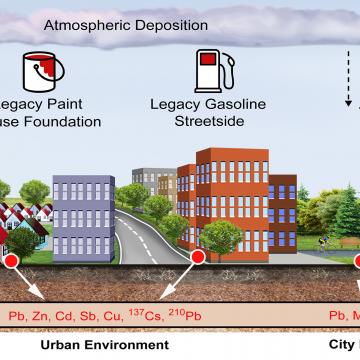
NewsA new Duke University study finds that municipal waste incinerators' legacy of contamination could live on in urban soils.
-
NewsKnowing voters have seen news reports about problems caused by failing or outdated public infrastructures in their district makes local officials who face competitive re-elections more inclined to support new spending to repair or replace the aging structures, a survey of city and county officials in 49 states shows. Findings from the survey by Duke University and the Environmental Policy Innovation Center underscore the continued importance of local media even as newsrooms shrink nationwide.
-
NewsThe sustainability of North American forests depends on trees’ ability to produce seeds and seedlings that can survive and grow in a changing climate. A new Duke University-led research initiative with more than $2 million in funding from the National Science Foundation aims to help boost their odds of success.
-
NewsSlashing emissions of carbon dioxide by itself isn’t enough to prevent catastrophic global warming, a new study shows. But if we simultaneously also reduce emissions of methane and other often overlooked climate pollutants, we could cut the rate of global warming in half by 2050 and give the world a fighting chance.
-
NewsA forest’s ability to regenerate after devastating wildfires, droughts or other disturbances depends largely on seed production. Findings from two new studies led by Duke University researchers could boost recovery and replanting after these disasters by providing foresters with new guidance on which tree species produce more seeds and how their productivity can vary from location to location.
-
NewsUsing satellite images, scientists have detected hundreds of very large and previously unreported methane releases at oil and natural gas production sites across the globe.
-
NewsScientists, led by alumna Jacqueline Gerson PhD'21 and faculty member Emily Bernhardt, recorded the highest levels of atmospheric mercury pollution in the world in a pristine patch of the Peruvian Amazon
-
NewsMany North American tree species have begun to slowly migrate northward in response to global warming, but western and eastern forests are responding differently. A new Duke-led study reveals why.
-
NewsBy distinguishing between lead from modern sources and lead from pre-1970s vehicle exhaust fumes and leaded paint, the new test may be especially useful for assessing the hidden risks of legacy contamination.
-
NewsAs trees age and grow, it seems logical to assume their seed production will continue to grow, too, but a Duke-led study of 597 species worldwide nips that assumption in the bud.