-
NewsUsing a bedroom air filter that traps fine particles of pollution with diameters smaller than 2.5 micrometers can significantly improve breathing in asthmatic children, a new study by American and Chinese scientists shows.
-
NewsReforestation has been shown to cool surface temperatures, and a novel study suggests it may also reduce air temperature up to several stories above the ground.
-
NewsContaminants that occur together naturally in groundwater under certain geological conditions may heighten health risks for millions of North Carolinians whose drinking water comes from private wells, and current safety regulations don’t address the problem, a new Duke University study finds.
-
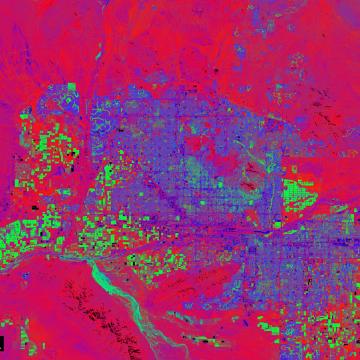
NewsScientists have devised a simple new model that explains how the undesirable effects of urban heat islands vary across seasons. Their results could help cities in different climatic regions design heat mitigation strategies.
-
NewsChronic exposure to microplastic fibers causes aneurysms, erosion of surface layers and other serious damage to fish gills, and increases egg production in female fish, a sign that chemicals in the fibers may be acting as endocrine disruptors, a new study by U.S. and Chinese scientists finds.
-
NewsThe North Carolina Climate Science Report benefits from the scientific expertise of two Nicholas School of the Environment faculty members.
-
NewsA team of students from the Nicholas School of the Environment and Pratt School of Engineering has been working for more than a year to create a single digital map of the service boundaries of North Carolina’s drinking water systems.
-
NewsThe ratio of carbon isotopes in three common species of tuna has changed substantially since 2000, suggesting major shifts are taking place in phytoplankton populations that form the base of the ocean’s food web, a new international study finds.
-
NewsA new study which combines measurements from nearly 1,400 drinking water wells across North Carolina estimates that more than half of the wells in the state’s central region contain levels of cancer-causing hexavalent chromium in excess of state safety standards.
-
NewsInhaling dust that contains fly ash particles from coal combustion has been linked to lung and heart disease, cancer, nervous system disorders and other ill effects. But tracking the presence of coal ash in dust has been a challenge for scientists.
-
NewsPredicting if droughts and heat waves will kill forests is difficult, but new work by scientists and engineers at Duke, Princeton, Stanford and the University of Alabama (UA) could help scientists spot problems early enough that they can still mitigate the threats and help restore at-risk forests.
-
NewsLocal conservation can boost the climate resilience of coastal ecosystems, species and cities and buy them precious time in their fight against sea-level rise, ocean acidification and warming temperatures, a new paper by scientists at Duke University and Fudan University suggests.
-
NewsDuke University has received a five-year, $5 million grant from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) to develop a new environmental analysis laboratory.
-
NewsWith the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) poised to loosen coal ash rules for dry onsite storage and large fill projects, a new study from Duke University finds that leaving those contaminants exposed may significantly heighten the risk of toxic contamination to nearby soil and waterways.
-
NewsAllowing coal ash to be spread on soil or stored in unlined pits and landfills will raise the risk that several toxic elements, including carcinogenic hexavalent chromium, could leach out of the coal ash and contaminate nearby water supplies across the U.S., according to preliminary findings from a new Duke University study.