-
NewsUrban ecologists developed a new approach to understanding biodiversity patterns in cities. The work could inform efforts to improve access to nature’s benefits.
-
NewsPh.D. students Keqi He, Rafaella Lobo honored for their respective scholarship.
-
NewsMeet the Silliman Lab, learn more about its research focus, a PhD student's experience in the lab and the opportunities the lab offers Duke students.
-
NewsMaintaining a water level between 20 and 30 centimeters below the local water table will boost southern peatlands’ carbon storage and reduce the amount of greenhouse gases they release back into the atmosphere during dry periods by up to 90%, a Duke University study finds.
-
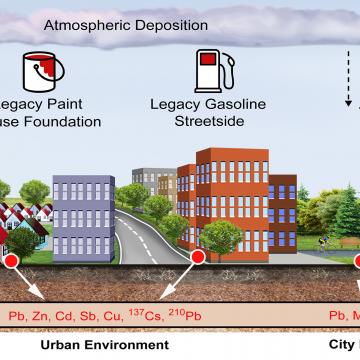
NewsA new Duke University study finds that municipal waste incinerators' legacy of contamination could live on in urban soils.
-
NewsBrian R. Silliman, Rachel Carson Distinguished Professor of Marine Conservation Biology at Duke University’s Nicholas School of the Environment, has been elected a Fellow of the Ecological Society of America (ESA).
-
-
NewsThe National Science Foundation and the Paul G. Allen Family Foundation have awarded a $1.2 million grant to support a new initiative aimed at boosting ecosystem restoration and climate resilience along North Carolina’s coast.
-
NewsKnowing voters have seen news reports about problems caused by failing or outdated public infrastructures in their district makes local officials who face competitive re-elections more inclined to support new spending to repair or replace the aging structures, a survey of city and county officials in 49 states shows. Findings from the survey by Duke University and the Environmental Policy Innovation Center underscore the continued importance of local media even as newsrooms shrink nationwide.
-
NewsRewetting and restoring 250,000 acres of southern pocosin peatlands that had been drained for farming but now lie fallow could prevent 4.3 million tons of climate-warming carbon dioxide, now stored in their soils, from oxidizing and escaping back into Earth’s atmosphere each year, a Duke University study shows. That amount equals 2.4% of the total annual reductions in CO2 emissions needed for the United States to be carbon neutral by 2050.
-
NewsHuman activities such as marsh draining for agriculture and logging are increasingly eating away at saltwater and freshwater wetlands that cover only 1% of Earth’s surface but store more than 20% of all the climate-warming carbon dioxide absorbed by ecosystems worldwide. A new study published May 5 in Science by a team of Dutch, American and German scientists shows that it’s not too late to reverse the losses.
-
NewsCoastal marshes that have been invaded by feral hogs recover from disturbances up to three times slower than non-invaded marshes and are far less resilient to sea-level rise, extreme drought and other impacts of climate change.
-
NewsBy distinguishing between lead from modern sources and lead from pre-1970s vehicle exhaust fumes and leaded paint, the new test may be especially useful for assessing the hidden risks of legacy contamination.
-
NewsA partnership between Duke University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, the new concurrent Master of Environmental Management/Master of City and Regional Planning provides training to those seeking to solve environmental issues within an urban context.
-
NewsDecades after federal bans ended widespread use of lead-based paint and gasoline, some urban soils still contain lead levels that exceed safety guidelines for children.