-
NewsDuke experts discuss how the legislation spurred environmental progress in America
-
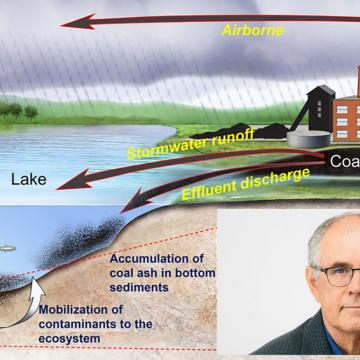
NewsToxins in lake bottom may become available to food web
-
NewsMixing toxic coal ash into acid mine drainage may sound like an odd recipe for an environmental solution, but a new Duke University-led study finds that it can neutralize the drainage’s dangerously low pH and help reduce harmful impacts on downstream ecosystems—if you use the right type of ash. Using the wrong type of ash can create new contamination and not tame the drainage’s extreme acidity.
-
NewsResearchers at Duke University have received a $248,000 grant from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency to study PFAS exposure risks in the home environment.
-
NewsFirefighters have a 9 percent higher risk of being diagnosed with cancer and a 14 percent higher risk of dying from the disease than the general adult U.S. population, according to studies by the National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health and other agencies.
-
NewsKate Hoffman, an assistant research professor at Duke University’s Nicholas School of the Environment, has received a $3.4 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to study the impact of early-life exposures to semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) on neonatal and early childhood immune function.
-
NewsProducing energy from fossil fuels uses or contaminated much more water than previously estimated, a new book by two Duke researchers shows.
-
NewsDuke researchers implement a large water sampling campaign in rural Sri Lanka, aiming to discover the origins of a cluster of chronic kidney disease cases.
-
NewsThe anti-fogging sprays and cloths many people use to prevent condensation on their eyeglasses when wearing a mask or face shield may contain high levels of per- and polyfluorinated alkyl substances (PFAS), a new Duke University-led study finds.
-
NewsUsing data gleaned from the spread of COVID, researchers have created a mathematical model that can predict where pandemics or contagious disease outbreaks will most likely spread, in what patterns, and how quickly.
-
NewsShannon Switzer Swanson MEM'15 hosts the documentary, “The Last Drop.”
-
NewsIn "Streams of Revenue: The Restoration Economy and the Ecosystems It Creates,” Martin Doyle chronicles and analyzes the history, implementation and environmental outcomes of stream mitigation banking, one of many widely used market-based approaches to conservation.
-
NewsThe proliferation of pits and ponds created in recent years by miners digging for small deposits of alluvial gold in Peru’s Amazon has dramatically altered the landscape and increased the risk of mercury exposure for indigenous communities and wildlife, a new study shows.
-
NewsGroundwater depletion in parts of the High Plains is so extreme that peak grain production in some states has ended and production is now declining, a new Duke University-led study by a team of international scientists finds.
-
NewsMan’s best friend may also be man’s best bet for figuring out how environmental chemicals could impact our health. Researchers from North Carolina State University and Duke University’s Nicholas School of the Environment used silicone dog tags as passive environmental samplers to collect information about everyday chemical exposures, and found that dogs could be an important sentinel species for the long term effects of environmental chemicals.