-
NewsMixing toxic coal ash into acid mine drainage may sound like an odd recipe for an environmental solution, but a new Duke University-led study finds that it can neutralize the drainage’s dangerously low pH and help reduce harmful impacts on downstream ecosystems—if you use the right type of ash. Using the wrong type of ash can create new contamination and not tame the drainage’s extreme acidity.
-
NewsProducing energy from fossil fuels uses or contaminated much more water than previously estimated, a new book by two Duke researchers shows.
-
NewsDuke researchers implement a large water sampling campaign in rural Sri Lanka, aiming to discover the origins of a cluster of chronic kidney disease cases.
-
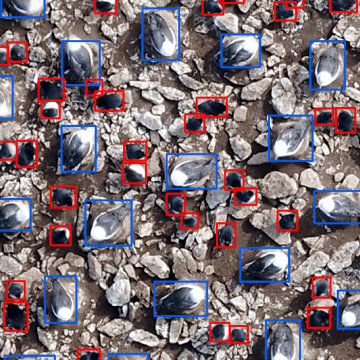
NewsUsing drones and artificial intelligence to monitor large colonies of seabirds can be as effective as traditional on-the-ground methods while reducing costs, labor and the risk of human error, a new study finds.
-
NewsShannon Switzer Swanson MEM'15 hosts the documentary, “The Last Drop.”
-
NewsThe WildTrack Specialist Group, a global network of biologists and conservationists dedicated to using only non-invasive techniques to monitor and protect endangered species, will be launched April 22 to celebrate Earth Day.
-
NewsOcean mammals are at a crossroads, with some species at risk of extinction and others showing signs of recovery, a new study by an international team of researchers shows.
-
NewsIn "Streams of Revenue: The Restoration Economy and the Ecosystems It Creates,” Martin Doyle chronicles and analyzes the history, implementation and environmental outcomes of stream mitigation banking, one of many widely used market-based approaches to conservation.
-
NewsThe proliferation of pits and ponds created in recent years by miners digging for small deposits of alluvial gold in Peru’s Amazon has dramatically altered the landscape and increased the risk of mercury exposure for indigenous communities and wildlife, a new study shows.
-
NewsGroundwater depletion in parts of the High Plains is so extreme that peak grain production in some states has ended and production is now declining, a new Duke University-led study by a team of international scientists finds.
-
NewsInteractive software that “reads” and analyzes footprints left by black rhinoceroses can be used to monitor the movements of the animals in the wild, giving conservationists a new way to keep watch on the endangered species and help keep it safe from poachers, according to a Duke University-led study.
-
NewsScientists at Duke University are harnessing the power of big data and geospatial analysis to create new ways to track the effects of climate change on species and food webs.
-
NewsSmall-scale gold mining in the Peruvian Amazon poses a health hazard not only to the miners and communities near where mercury is used to extract gold from ore, but also to downstream communities hundreds of kilometers away where people eat mercury-contaminated river fish as part of their diet.
-
NewsReusing low-saline oilfield water mixed with surface water to irrigate farms in the Cawelo Water District of California does not pose major health risks, as some opponents of the practice have feared, a study led by Duke University and RTI International researchers finds.
-
NewsThe Migratory Connectivity in the Ocean (MiCO) system, an online open-access global database that maps the movements of sea turtles, whales, sea birds and other migratory species through the open ocean, has been awarded the 2020 Innovation Award by the Ocean Awards program.